TendoMax
For the treatment of pain and limited mobility occurring in tendon problems
TendoMax
- Na-hyaluronate 40mg/2ml
- Mannitol 10mg/2ml
Sterile, viscoelastic solution for peritendinous or tendon sheath application, indicated for the treatment of pain and limited mobility occurring in tendon problems.
Composition:
It consists of linear chains of sodium hyaluronate, of medium molecular weight (2.4 x 106 Dalton), obtained by fermentation of the bacterial strain Streptococcus, and mannitol.
This molecular weight promotes strong binding to fibroblast receptors, activation of a large number of receptors and stimulation of endogenous biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid.
Method of administration:
Inject a dose along the damaged tendon (but not into the tendon itself) or into the sheath of the tendon at the damaged place once a week, up to a total of 2 injections.
Multiple tendons can be treated at the same time.
The treatment can be repeated as needed.
Tendinitis (tendinopathy) is a condition characterized by tendon inflammation caused by overuse, injury, or other medical conditions. It is accompanied by the following symptoms and signs: pain, swelling, redness, elevated temperature…
Tendosynovitis is inflammation of the sheath of the tendon.
Forms of tendinitis:
-
elbow tendinitis,
-
shoulder tendinitis,
-
knee tendinitis,
-
wrist tendinitis,
-
Achilles tendinitis,
-
ankle tendinitis
Tendinitis in the elbow joint
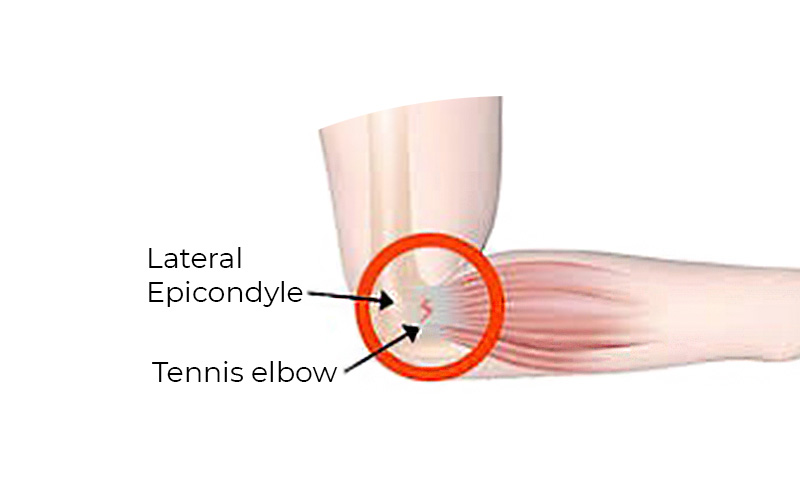
- Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) – causes pain on the outside of the elbow joint
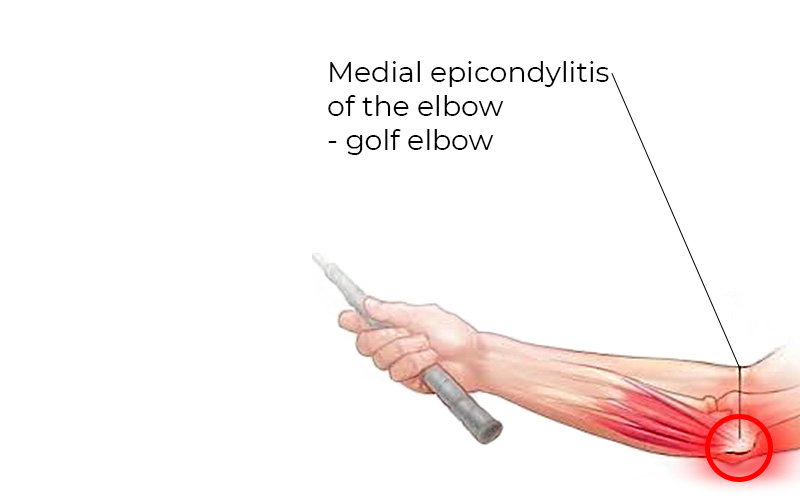
- Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow) – causes pain on the inside of the elbow
Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) – causes pain on the outside of the elbow joint
Medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow) – causes pain on the inside of the elbow
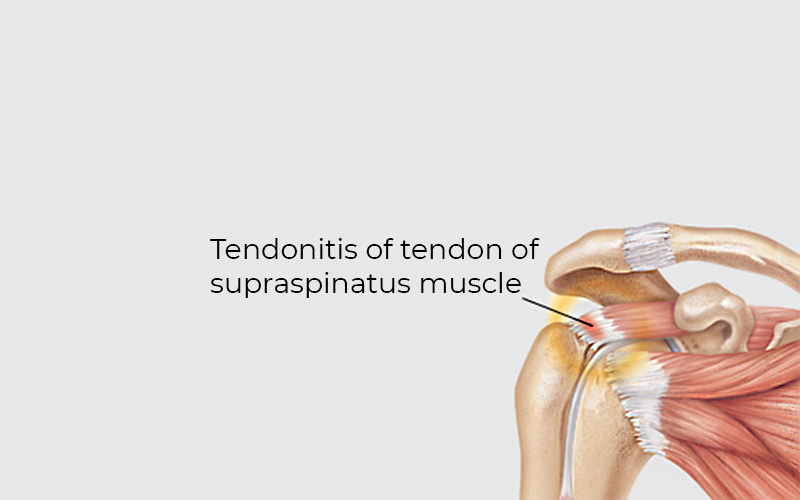
Tendinitis of the shoulder joint
Tendinitis of the shoulder joint (inflammation of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles) – includes the tendons of m. supraspinatus which attaches to the upper part of the humerus at the shoulder joint.
Tendinitis of the knee joint (“jumper’s knee”)
Tendinitis of the knee joint (“jumper’s knee”) – inflammation of the patellar tendon, occurs as a result of knee overload, most often in athletes.
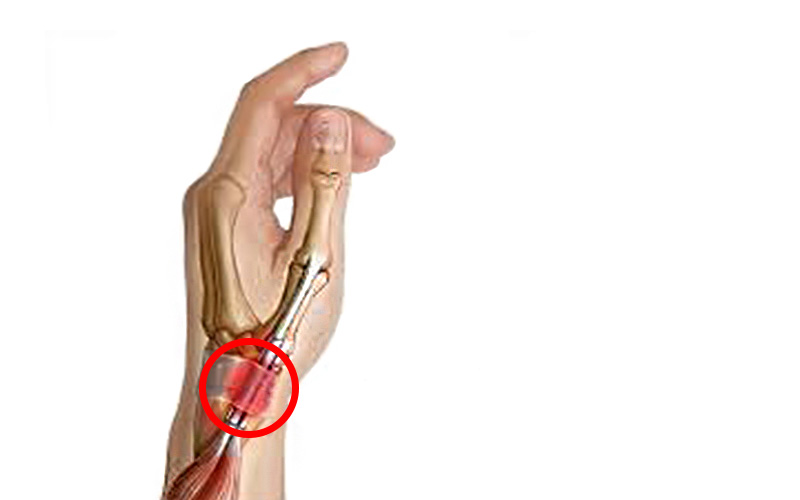
Tendinitis in the wrist
Tendinitis in the wrist usually occurs in the form of De Quervain’s syndrome, the most common type of tendon sheath inflammation affecting the tendons of the thumb. Characteristic symptoms are pain and swelling at the root of the thumb, as well as difficulty moving the thumb and wrist during certain movements. If they are not treated adequately, the painful region can spread to the entire thumb and along the forearm.
Tendinopathy of the Achilles tendon
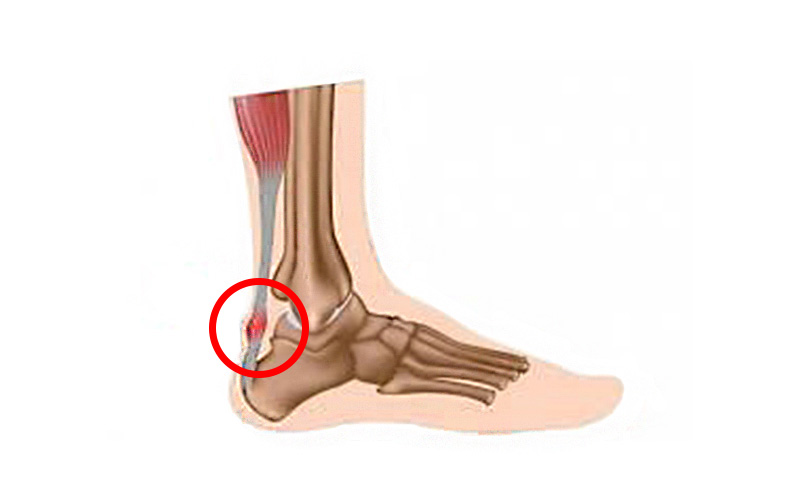
Achilles tendinitis is an acute inflammation of the tendon that occurs due to the simultaneous action of several factors (high training load, uneven surface, insufficient rest). It causes swelling of the Achilles tendon and unpleasant pain.
Achilles tendon enthesitis is an inflammatory process localized at the very attachment of the tendon to the heel bone. This tendinopathy is more persistent than tendinitis and requires longer treatment.
Achilles tendinopathy is sometimes associated with inflammatory diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis, gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
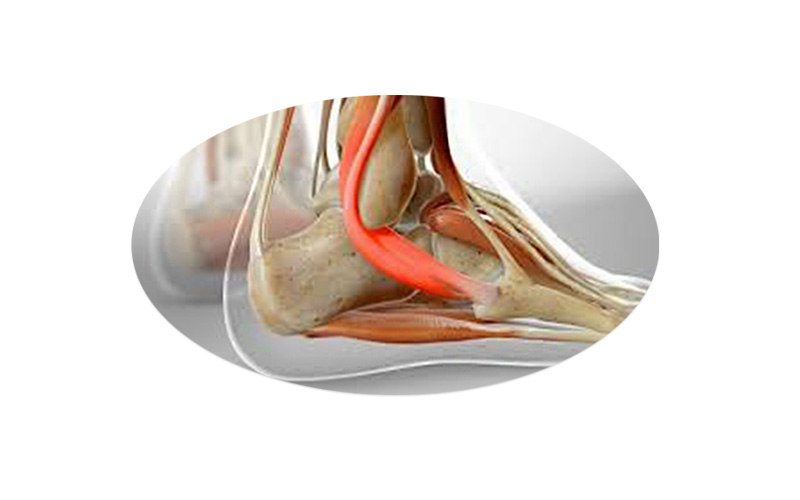
Ankle tendinitis (peroneal tendinitis)
Ankle tendinitis (peroneal tendinitis) inflammation of the peroneal tendon that lies behind the lateral malleolus.
Peroneal tendinitis often occurs during the healing phase of an ankle sprain because the ankle becomes weak and unstable, causing the peroneus to work harder to provide the necessary support to the damaged lateral ligaments of the ankle.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is a typical glycosaminoglycan (GAG), the only one that exists free, not bound to proteins.
Sodium hyaluronate is made of disaccharide units consisting of sodium glucuronate and N-acetylglucosamine. It is present in all tissues, is highly biocompatible and forms the main component of synovial fluid, where it is found in high concentration.
Clinical studies have shown that peritendinous application of hyaluronic acid is a safe and effective therapeutic option for the treatment of chronic tendinopathy.
Effects of hyaluronic acid in tendinopathies:
- It has a lubricating effect
- It has an anti-inflammatory effect
- It affects cell repair
- It has an analgesic effect
- Reduces the need for physical therapy
Mannitol
In addition to its anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effects, mannitol exhibits a strong antioxidant effect. Mannitol protects hyaluronic acid from degradation caused by free radicals, increases its retention time, without significant modification of the rheological behavior → therefore prolongs the duration of action of hyaluronic acid and its effectiveness.
In addition, mannitol has a very good safety profile even at high doses.
Clinical studies have confirmed the effectiveness of hyaluronic acid in combination with mannitol in the treatment of various forms of tendinopathies.
Instructions for use (pdf 3.22 MB)
Write to us
Mosorska 9, 11000 Belgrade, Serbia
Vemax011 Pharma doo representative office Northern Macedonia - Dane Krapcev 13, Skopje
Vemax011 Pharma doo representative office Montenegro - Topliški put 1, Budva
Vemax011 Pharma doo representative office Bosnia and Hercegovina - Vlakovo 252, Sarajevo
+381 (0)63 103 00 08
office@vemaxpharma.rs
Vemax Pharma - your trusted regional partner on the road to health!